You might only associate a heat rash with babies. But hot, humid weather puts children of all ages at a higher risk of developing a heat rash, too. Some people refer to heat rash as “prickly heat.”
When it’s hot out, there’s an increased risk for active children to develop a heat rash, especially if they’re playing outside, overdressed for the weather or wearing clothes that don’t allow their skin to breathe. These factors may increase the amount of sweat on your child’s skin, which then increases the chance of a heat rash developing.
“Excessive sweating may cause a child’s pores, which are sweat gland ducts, to become blocked. The perspiration can then become trapped underneath the skin,” explains pediatrician Paula Sabella, MD. “This may result in skin irritation, redness and sometimes an itchy rash, known as heat rash.”
From an infant to a toddler to a child, heat rash is common, especially during warmer months. Dr. Sabella explains what to look for and how to prevent heat rash.
What does heat rash look like in children?
So, what does heat rash look like?
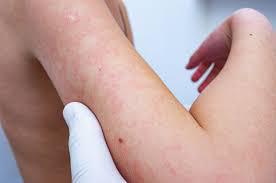
Children’s heat rash may look like tiny bumps surrounded by red skin. And kids may experience a prickly sensation, but it usually isn’t painful.
In infants, the rash generally develops on their neck, armpits, elbow creases and groin. In older children, it may also occur on their chest and back. Typically, a heat rash doesn’t involve the eyes, nose, mouth, palms or soles.
“If your child develops a heat rash, you can expect that they will act normally,” says Dr. Sabella. “A child with a heat rash shouldn’t have a fever or other signs of illness.”
How to get rid of heat rash
If you suspect your child has a heat rash, you should start the cool down process right away. Dr. Sabella offers these tips:
Immediately get your child out of the heat and into a cooler area.
Use a fan to cool your child.
Remove any extra clothing that your child may be wearing.
Use a cool, damp washcloth on their skin to remove sweat and body oils.
Give your child a lukewarm bath or shower.
Dry off any excess moisture.
“There is no need to use any lotions, oils, creams or ointments on the skin, as this could further block the pores, trap moisture and make the heat rash worse,” cautions Dr. Sabella.
A heat rash typically clears up in a few days on its own and leaves no permanent damage to the skin. And a heat rash isn’t contagious.
How to prevent it in the future
Blocked sweat glands cause a heat rash, so it’s important to try and stay cool and dry. Keep these factors in mind, as they may contribute to heat rash:
Hot, humid weather or environment.
Physical activity, intense exercise, hard work or activity.
Fabrics that don’t allow sweat to evaporate from the skin.
Overdressing your child or dressing in too heavy of fabric for the weather.
Sleeping under too many blankets.
Application of oils, thick creams or ointments.
Remember to dress your child in a breathable fabric like cotton, which allows the air to circulate and enables the sweat to evaporate. This will keep your child’s skin cool and dry and will hopefully minimize the risk of developing a heat rash.
When to see the doctor
Typically, heat rash on babies, toddlers and children doesn’t require medical attention. But be sure to call your pediatrician if the heat rash persists, doesn’t improve in a few days, is getting worse, if you’re worried or if you see signs of infection.
Signs of infection could be in the form of:
Fever or chills.
Pain, swelling, redness or warmth around the affected area.
Blisters or scabs.
Swollen lymph nodes in the armpit, neck or groin.
“It’s important to seek medical care if your child has fever or signs of infection, is acting sick or has any other symptoms,” advises Dr. Sabella.
Source: Cleveland Clinic
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/how-to-cool-your-childs-heat-rash/
 FR
FR EN
EN AR
AR








